Japan Time Zone, officially JST (Japan Standard Time), is nine hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). This consistent time zone, unlike many others that observe Daylight Saving Time, plays a significant role in shaping daily life, business operations, and international collaborations for Japan. Understanding its history, its impact on society, and its interaction with technology provides valuable insight into the complexities of timekeeping in a globalized world.
This exploration delves into the historical evolution of Japan’s time zone, examining key changes and comparing it to neighboring countries. We’ll analyze the reasons behind Japan’s decision against Daylight Saving Time, considering both potential benefits and drawbacks. Further, we will explore the influence of technology on accurate timekeeping in Japan and consider potential future adjustments to the time zone.
Japan’s Time Zones: Japan Time Zone
Japan observes a single time zone, Japan Standard Time (JST), which is UTC+9. This means that Japan is nine hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). This consistent timekeeping across the archipelago simplifies daily life and facilitates national communication and coordination.
Japan’s Time Zone History
The adoption and adjustment of Japan’s time zone has been a gradual process, reflecting the nation’s modernization and its integration into the global community. Initially, various local times were used across different regions. The standardization of time began in the late 19th century, influenced by the increasing need for efficient railway operations and communication. In 1886, the Meiji government adopted a standard time based on the meridian passing through Tokyo, which was essentially UTC+9.
While there have been minor adjustments and proposals for daylight saving time (DST) over the years, Japan has consistently maintained its UTC+9 time zone without seasonal shifts. The lack of DST adoption is a complex issue involving various societal and economic considerations.
Comparison with Neighboring Countries’ Time Zones
Japan’s time zone differs from its immediate neighbors. South Korea, for instance, also observes a single time zone, Korea Standard Time (KST), which is UTC+9, making it the same as Japan. However, countries like China observe multiple time zones due to its vast geographical expanse. Russia, another neighboring country, uses a wide range of time zones due to its size.
These differences highlight the complexities of time zone management, particularly in geographically large nations.
Time Difference with Major World Cities
The following table displays the time difference between Japan Standard Time (JST) and major cities around the globe. This information is crucial for international communication, travel, and business dealings.
Japan operates on Japan Standard Time (JST), nine hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Understanding this time difference is crucial for international collaborations, and comparing it to other regions highlights these variations. For instance, consider the time difference with the wisconsin time zone , which further emphasizes the complexities of global timekeeping. Returning to JST, this consistent time zone simplifies scheduling within Japan itself.
| City | Time Difference (JST) | City | Time Difference (JST) |
|---|---|---|---|
| London, UK | -8 hours | New York, USA | -13 hours |
| Paris, France | -7 hours | Los Angeles, USA | -16 hours |
| Berlin, Germany | -7 hours | Sydney, Australia | +1 hour |
| Moscow, Russia | -6 hours | Toronto, Canada | -14 hours |
Standard Time and Daylight Saving Time in Japan

Japan, a nation known for its precision and adherence to schedules, operates on a single time zone throughout the year: Japan Standard Time (JST), which is UTC+9. Unlike many Western nations, Japan does not observe Daylight Saving Time (DST). This consistent timekeeping approach has been in place for decades and significantly shapes the daily lives of its citizens and its economic activities.Japan’s unwavering commitment to Standard Time stems from a variety of factors, primarily focusing on minimizing disruption and maintaining operational efficiency across its diverse industries.
The potential complexities and costs associated with transitioning between Standard Time and DST are deemed to outweigh any perceived benefits. The highly structured nature of Japanese society and its emphasis on punctuality and synchronized schedules further reinforces this preference for a consistent time system.
Reasons for Japan’s DST Policy (or Lack Thereof)
The absence of DST in Japan is a deliberate policy choice rooted in practical considerations. The primary reason is the minimization of disruption to the daily routines of its citizens and businesses. A shift in time would necessitate adjustments to work schedules, transportation systems, and various other aspects of daily life. Given the highly organized and time-sensitive nature of Japanese society, the potential for confusion and inefficiency is considered too high a price to pay.
Furthermore, the relatively short daylight hours during winter months are not deemed to warrant the inconvenience of a time change. The perceived benefits of extending daylight into the evening are outweighed by the significant operational challenges of implementing and managing a DST system.
Potential Economic and Social Impacts of Implementing DST in Japan
While the potential economic benefits of DST, such as reduced energy consumption, have been debated globally, the implementation in Japan presents unique challenges. The highly synchronized nature of Japanese industries, particularly manufacturing and transportation, suggests that the disruption caused by a time change could significantly outweigh any potential energy savings. For example, the coordination of just-in-time manufacturing processes, reliant on precise timing and scheduling, would be severely hampered by a DST shift.
Similarly, the intricate scheduling of public transportation networks would require extensive adjustments, leading to potential delays and operational inefficiencies. Socially, the disruption to established routines and the potential for confusion among the population would pose significant challenges. The ingrained adherence to precise timekeeping in Japan suggests a strong resistance to the potential disruption caused by a time change.
Infographic: Yearly Time Changes in Japan
The infographic would depict a simple, clean design. The central element would be a large, bold display of “Japan Standard Time (JST): UTC+9” spanning the entire year. Below this, a horizontal timeline representing the 12 months of the year would be shown. Each month would be clearly labeled, and there would be no indication of time changes or daylight saving shifts.
The overall message would be the consistent and unchanging nature of JST throughout the year. A small inset graphic could show a stylized clock face set permanently at 9:00 AM to visually represent the unchanging time zone. The color scheme would be simple and understated, using shades of blue and grey to convey a sense of stability and reliability.
The Impact of Time Zone on Japanese Society

Japan’s adherence to Japan Standard Time (JST), which is UTC+9, significantly shapes the daily rhythms and operational dynamics of its society. This fixed time zone, unlike those employing daylight saving time, creates a consistent, albeit sometimes challenging, framework for the nation’s activities. The impact is felt across various aspects of life, from personal schedules to international business collaborations.
Daily Life in Japan’s Time Zone
The impact of JST on daily life is pervasive. Citizens’ waking hours, work schedules, mealtimes, and social engagements are all organized around this time frame. For instance, the typical workday begins relatively early, aligning with the global business practices of East Asia. This early start means that many Japanese citizens have already begun their workdays before sunrise during the winter months, and conversely, are finishing their days after sunset during the summer.
This pattern influences everything from commuting patterns (heavy rush hour traffic in the morning and evening) to the timing of social events and family dinners. The consistency of JST, however, provides a predictable structure to daily routines, fostering a sense of order and routine for many.
Challenges for Businesses Operating in JST, Japan time zone
Japan’s time zone presents both opportunities and challenges for businesses. The significant time difference between Japan and major Western markets (such as the US and Europe) necessitates careful scheduling of meetings and communications. Coordinating with international partners often involves working outside of standard business hours, requiring flexibility and potentially leading to fatigue. Furthermore, the early start to the Japanese business day can sometimes make it difficult to engage effectively with counterparts in other time zones who are still working late into the night or just starting their day.
This time difference can also affect trading activities on global financial markets, requiring businesses to adapt their operational strategies.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Japan’s Current Time Zone
The benefits of maintaining JST are primarily centered around consistency and predictability. A fixed time zone without the biannual adjustments of daylight saving time simplifies scheduling and eliminates the disruption caused by clock changes. This stability is particularly beneficial for industries with intricate logistical chains, such as manufacturing and transportation. However, the drawback lies in the significant time difference from major Western markets.
This difference can hinder real-time communication and collaboration, leading to potential inefficiencies and missed opportunities for business development. The lack of daylight saving time also means that during winter, working hours often overlap with periods of darkness, which can impact productivity and energy consumption.
Influence of Japan’s Time Zone on International Collaborations
Japan’s time zone significantly influences its international collaborations. The considerable time difference between Japan and many key global partners necessitates careful planning and flexible working arrangements. For example, holding virtual meetings requires careful consideration of participants’ time zones, potentially leading to meetings at inconvenient hours for one or more parties. This challenge is further amplified by the need for real-time communication in areas such as crisis management or collaborative projects with tight deadlines.
Despite these challenges, Japan’s strategic position in Asia and its strong economic ties worldwide mean that effective strategies for bridging time zone differences are crucial for maintaining its global competitiveness.
Japan’s time zone, a seemingly simple aspect of daily life, has profound implications for its citizens, businesses, and international relations. From the practical challenges of scheduling international meetings to the subtle ways it shapes daily routines, understanding JST is crucial to appreciating the complexities of modern Japan. While the future may hold potential adjustments, the current system continues to play a vital role in the country’s economic and social fabric.
FAQ Corner
What is the time difference between Japan and the US East Coast?
Japan is 13 hours ahead of the US East Coast.
Does Japan use 24-hour time?
While both 12-hour and 24-hour time formats are used, the 24-hour clock is more prevalent in formal settings and public transportation schedules.
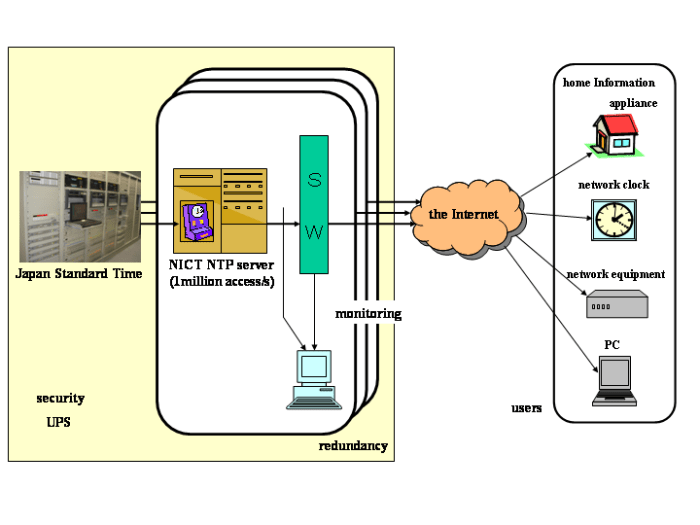
How accurate are the time servers in Japan?
Japan’s time servers maintain high accuracy, typically within a few milliseconds of UTC, utilizing atomic clocks and sophisticated synchronization techniques.
What are some challenges faced by Japanese businesses due to the time difference with Europe?
Challenges include coordinating meetings across time zones, managing overnight communication, and potentially impacting employee work-life balance due to extended working hours.